A Rack Server, commonly referred to as a rack-mounted server, is a computer dedicated to be used as a server and designed to be installed in a framework called a rack. The rack contains multiple mounting slots called bays, each designed to hold a hardware unit secured in place with screws. Rack mount servers drastically reduce the physical space required compared to traditional freestanding servers. They are commonly used for computing functions requiring high processing power such as web hosting, data analysis, and cloud computing. The configuration can consist of different server hardware including processors, memory, storage, and network capabilities, all tailored to an organization’s specific needs. The rack server chassis houses and protects these components, offering a convenient and organized solution for managing high-end computing tasks.

Different Types of Rack Servers
Rack mount servers are available in a range of sizes and styles, offering organizations flexibility to choose an ideal configuration that meets their specific needs. From tower server chassis for enterprise-level computing to mini 1U rackmount chassis for small businesses or home users, there is an option to fit any application. Many models also include features such as hot-swappable hard drives, redundant power supplies for improved uptime, and integrated RAID controllers for secure storage. There are several different types of rack servers, each designed to meet specific requirements in terms of performance, scalability, and budget.
1U Servers:
The ‘U’ in 1U stands for ‘unit’, indicating the height of the server. 1U servers are the smallest rack servers available and are an excellent choice for businesses that require high-performance computing in a compact form.
AX61120TB – 1U Rackmount Chassis
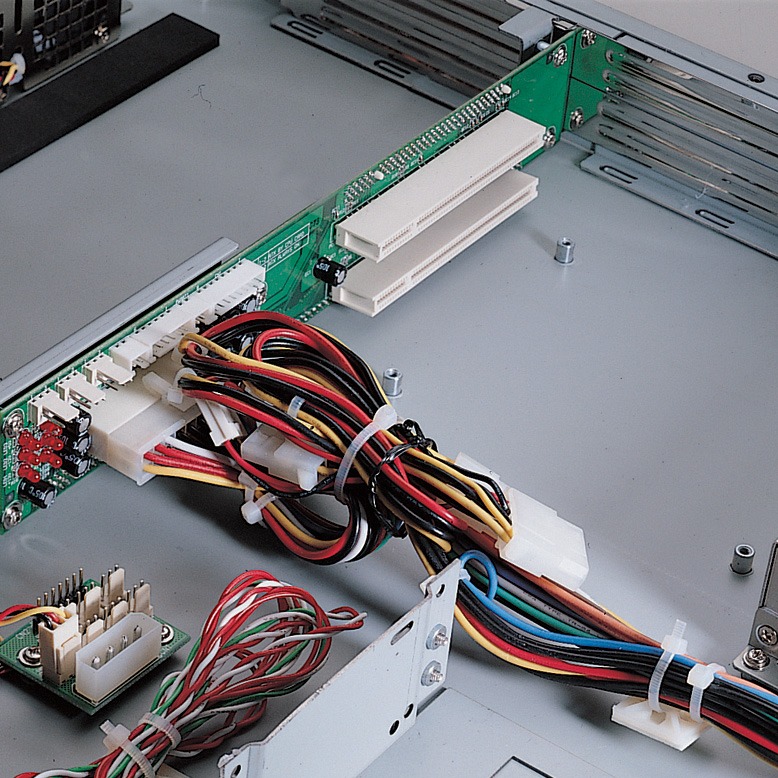
2U Servers:
These servers offer more space for additional hardware, such as extra hard drives or larger memory banks. They are ideal for organizations that require more computing power and storage capacity.
3U and 4U Servers:
These servers are larger and offer even more room for additional hardware components. They are ideally suited for organizations with particularly heavy computing needs, such as data centers and large enterprises.
Blade Servers:
These servers are designed to fit into a larger chassis, called a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers. Each containing its own processor, memory, storage, and network components.This design allows for high-density computing, making blade servers a good choice for businesses with significant server requirements. This allows organizations to maximize server power while utilizing minimal physical space.
Enterprise servers
These servers are full-size rack servers with powerful processors and large amounts of RAM for faster processing speeds. They are often used for large workloads such as data analysis and enterprise applications.
High-density servers
These servers are designed for compute-intensive applications such as virtualization, clustering, and cloud computing. Each server can hold up to four dual-socket processors and large amounts of RAM in a compact form, making them an ideal choice for organizations with data-heavy workloads.
Tower servers
These are stand-alone server systems that can also be mounted in a rack. They are designed to provide maximum expandability and flexibility while still delivering powerful computing performance.
In addition to these, there are other types of rackmount servers such as microservers, storage servers, GPU servers, and more. Each type of server has its own unique features and benefits that can help organizations scale up their IT infrastructure in a cost-effective manner.
Each of these types of rack servers offers its own set of advantages and potential use cases. By understanding the different options available, organizations can make informed decisions about which type of rack server will best meet their specific needs.
Essential Components Every Rack Server Chassis Should Include:
Rack servers contain various critical components that contribute to their effective functioning. Here’s a detailed insight into these components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU, also known as the server processor, is the brain of the server. Rack servers typically have more powerful CPUs than standard computers to handle large, complex data processes.
- Server Memory (RAM): Rack servers require substantial amounts of RAM to support multitasking and quick data access. More RAM allows the server to process larger amounts of data simultaneously and operate more efficiently.
- Storage Drives: Used to store the server’s operating system, applications, and data. Rack servers typically make use of redundant array of independent disks (RAID) storage systems for data redundancy and increased performance.
- Network Interface Cards (NICs): Rack servers usually have one or more NICs that enable them to connect to the network. These cards can be built into the server’s motherboard or added as expansion cards.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU provides electricity to all components of the server. Rack servers may have multiple PSUs for redundancy.
- Motherboard: The motherboard houses the server’s critical components, including the CPU, RAM, and storage. It also includes slots for expansion cards and interfaces for peripheral devices.
- Cooling Fans: Given the high-performance nature of rack servers, they generate significant heat. Cooling fans help to manage the heat and keep server components within their operational temperature ranges.
- Rack Rails: The server is attached to these rails to mount it safely and securely within the rack.
- Hardware RAID Controller: This component manages the physical disk drives and presents them to the computer as logical units.
- Server Operating System (OS): The OS manages the server’s hardware and software, including network connections, file storage, and application running.
Each component plays an essential role in ensuring the optimal functioning and efficiency of a rack server.
Key Features of Rack Mount Servers or Chassis:
Rack mount servers provide a variety of benefits, including increased efficiency and scalability, improved cooling systems, faster data access times, and enhanced security. With these features comes a greater ability to manage large amounts of data with fewer physical resources than traditional server configurations. Moreover, rack servers are compatible with other computer components and can be easily integrated into existing infrastructures.
- Space Efficiency: Rack mount servers are designed with a slim profile that conserves floor space, enabling the stacking of multiple servers within a single rack.
- Improved Cooling: The design of rack servers allows for better airflow between units, helping to keep the servers cool and reducing the risk of overheating.
- Scalability: Rack servers offer the flexibility to add more servers to the rack as business computing needs grow, making it a scalable solution.
- Easy Maintenance: Rack servers are designed for easy access, making it simpler for technicians to perform maintenance or replace components.
- Enhanced Security: The consolidated nature of rack servers allows for improved security measures, both physically (locked server racks) and in terms of network security.
- Reduced Clutter: With all servers housed in one place, there are fewer cables spread across the floor, reducing clutter and the risk of accidental disconnections or tripping hazards.
- Cost-Effective: Despite the initial investment, rack servers can prove to be cost-effective in the long run due to their scalability, ease of maintenance, and efficient use of space.
- High Performance: Rack servers are typically high performing machines capable of handling complex, resource-intensive tasks, making them a valuable asset for businesses.
- Power Management: Rack servers often share a common power source, making it easier to manage power supply and possibly reduce energy costs.
- Centralized Management: Rack servers enable centralized management of all servers within the rack, simplifying the monitoring and administration process.
Benefits of Having Rackmount Servers:
Rackmount servers are a fundamental component of many modern businesses, offering several benefits that facilitate improved operational efficiency and overall performance:
- Space Optimization: Rackmount servers are designed to be compact, which not only reduces the overall footprint in comparison to traditional tower servers, but also allows for higher server density. This efficient space utilization is particularly advantageous for businesses with limited physical space.
- Scalability: As business needs evolve, additional rackmount servers can be seamlessly integrated into the existing infrastructure. This ability to scale up operations without substantial overhaul is a significant advantage for growing businesses.
- Efficient Cooling: The design of rackmount servers permits excellent airflow, reducing overheating risks and promoting the longevity and stability of the servers.
- Centralized Management: By consolidating servers into one location, rackmount servers enable centralized control, simplifying server administration and management.
- Enhanced Security: Rackmount servers can be locked in cabinets to prevent unauthorized physical access. Additionally, centralized servers make it easier to implement and monitor network security measures.
- Cost-Effective: Over time, the efficiencies in space, power, and cooling can lead to significant cost savings, making rackmount servers a cost-effective solution for businesses.
Usefulness of Rackmount Servers:
Rackmount servers play a crucial role in the daily operations of a business. They handle a multitude of tasks, including hosting websites, managing emails, storing data, running applications, and more. Through their powerful processing capabilities, they enable businesses to manage large volumes of data quickly and efficiently. Furthermore, their scalability and ease of maintenance make them a sustainable choice for businesses, accommodating growth and changes over time. By facilitating secure, efficient, and scalable operations, rackmount servers are invaluable for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure.


